Newton’s First Law Of Motion
Newton's First Law of Motion, sometimes referred to simply as "the first law" is the most basic law of classical physics—a fundamental principle from which we can derive all other physics for the motion of an object. It was developed by Sir Isaac Newton back in the late 17th century. In simple terms, the law establishes that a body at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving uniformly in a straight line unless acted on by an external force. This principle emphasizes the innate tendency of objects to oppose changes in their state of motion.
This law is built on the concept of inertia. Inertia is the property of an object to resist changes in a body's motion. The greater the mass of an object, the greater the object's inertia. This results in more force needed to change its motion. For example, a large truck requires a larger force to speed up or slow down compared to that of a small automobile. This is owed to the larger inertia of the former. This concept is not only important for start board exam also for the competitive exam like JEE Main, NEET and another engineering exam like SRMJEE, VITEE, WBJEE and others.
JEE Main/NEET 2027: Physics Important Formulas for Class 10
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- Newton's First Law Of Motion
- Solved Example Based on Newton's First Law Of Motion
- Summary

Newton's First Law Of Motion
Newton’s 1st law of motion states that if the (vector) sum of all the forces acting on a particle is zero, then and only then does the particle remain unaccelerated, i.e., remains at rest or move with constant velocity.
If
Newton’s first law is also called the law of inertia.
Newton’s laws are valid in an inertial frame of reference but are not valid in a non-inertial frame of reference. Frame of reference
A frame of reference is a system of coordinate systems and clocks.
Types of frame of reference:
There are mainly two types of frame of reference one is internal frame of rfrefrance and another is a non internal frame of reference.
- Inertial frame of reference- A frame which is at rest or moving with uniform velocity.
Example- 1. Car moving with velocity v on a straight road, Lift at rest.
- A non-inertial frame of reference- A frame which is accelerated and does not have a constant velocity.
Example- 1. The frame travels in a straight line but speeding up or slowing down.
2. The frame travels along a curved path.
Recommended Topic Video
Solved Example Based on Newton's First Law Of Motion
Example 1: Choose the correct option.
In which Kind of motion an object in motion will stay in motion as long as the net forces acting on it are zero?
1) Slowing motion in a straight line
2) Accelerating motion in a straight line
3) Constant motion in a straight line
4) All of these
Solution:
As we learned
Newton’s 1st law of motion states that if the vector sum of all the forces acting on a particle is zero, then and only then does the particle remain unaccelerated, i.e., remains at rest or moves with constant velocity.
So for a Constant motion in a straight line if the net forces acting on it are zero then the object in motion will stay in motion.
Hence, the answer is the option (3).
Example 2:|Two blocks of masses

1) The block A moves down the plane
2) Block B moves down the plane
3) Both blocks remain at rest.
4) Both blocks move down the plane.
Solution

For block A :mg
Hence Both blocks remain at rest.
Example3 :A block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with an angle of inclination
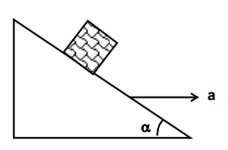
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution :

For block to remain stationary,
Hence, the answer is option (2).
Example 4: While pushing a very heavy box, Derek noticed that it was harder for him to get the box to start moving. This is an example of which mechanics principle?
1) Newton’s first law
2) Law of universal gravitation
3) Newton’s second law
4) Newton’s third law
Solution:
This is an example of Newton's first law: An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion in that direction unless acted upon by an outside force.
Inertia is effectively nature’s way of trying to avoid change. This explains why the box is hard to move while it is still; it requires a change to get it to move from rest to moving.
When we try to push a very heavy box kept on the ground, it does not move at all because the weight of the box and frictional force acting due to roughness between the contact surfaces prevent this box from moving forward.
Hence, the answer is option (1).
Example 5: A boy pushes a box of mass
1) 500
2) 100
3) 200
4) 600
Solution

Displacement along
Hence, the answer is option (1).
Summary
Newton's First Law underlies all the basic mechanics of the way objects move and interact. It leads immediately to the conclusion that in the absence of forces due to factors like friction or air resistance, for instance, an object will continue on its course indefinitely. This can be observed in space, where no proposed rocket propulsion is adapted in spacecraft yet it covers vast distances.
Understanding Newton's First Law is important because it applies to real-world situations, from everyday kinds of things such as pushing a shopping cart, to huge engineering projects, and it leads us into Newton's other two laws of motion and classical mechanics as a whole. Since this law lets us know that unless a force from an outside device is applied, motion (or not) will continue, it explains the natural actions that objects take and forms a foundation for logical progressions and applications of all more advanced notions in physics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An object in rest will remain in rest, and an object in motion will continue in a linear path with constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
The law of inertia
The inert property of the object is termed inertia.
Friction and other external forces are absent in space, so the spaceship continues linearly at a constant velocity.
Friction is an external force acting upon the objects that could change the state of the object's motion or increase the stalling of velocity.
For example, a book on a table would stay at rest until a person applies force to it to keep it in motion.
Also Read
21 May'25 12:19 PM
05 Feb'25 04:38 PM
11 Jan'25 03:12 PM
03 Dec'24 04:00 AM
03 Dec'24 03:48 AM
29 Nov'24 11:10 AM
28 Nov'24 01:12 AM
27 Nov'24 11:57 PM
27 Nov'24 02:41 PM
27 Nov'24 02:15 PM

