Electric Flux - Definition, Formula, FAQs
Electric flux measures how an electric field passes through an area that was defined already. Electric flux within electromagnetism is very important because it helps in proper comprehension of how electric fields come into contact with or affect surfaces. Over the last ten years of the JEE Main exam (from 2013 to 2023), nine questions have been asked on this concept. In this article, we will discuss what is electric flux class 12, the symbol of electric flux, the electric flux formula, properties of electric flux, Gauss's law, the SI unit, the dimension of electric flux, the derivation of electric flux through a closed surface and electric flux density.
JEE Main/NEET 2027: Physics Important Formulas for Class 10
NEET 2025: Mock Test Series | Syllabus | High Scoring Topics | PYQs
JEE Main: Study Materials | High Scoring Topics | Preparation Guide
JEE Main: Syllabus | Sample Papers | Mock Tests | PYQs
- What is Electric Flux Class 12?
- Electric Flux Formula
- SI Unit of Electric Flux and Dimensional Formula
- Properties of Electric Flux
- Electric Flux Density
- Gauss Law
- Derivation of Electric Flux Through a Closed Surface
- Solved Examples Based on Electric Flux

What is Electric Flux Class 12?
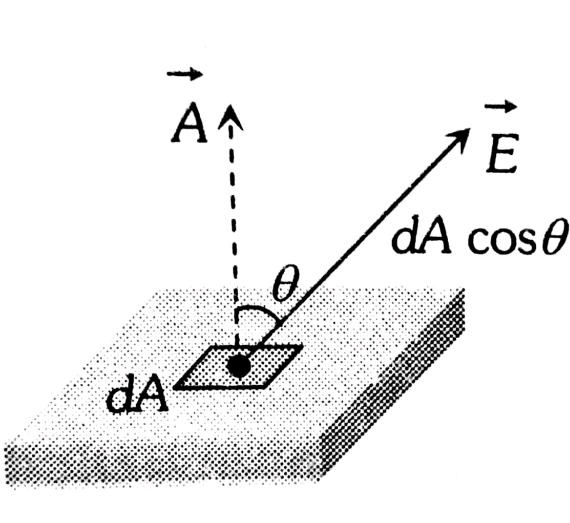
Electric flux definition: Electric flux is the rate of flow of electric lines of force across a particular area chosen as a surface.
Let us consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction. Let these field lines penetrate a rectangular surface of area A whose plane is oriented perpendicular to the field lines. The number of electric field lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field. So the total number of lines penetrating is proportional to
The symbol of electric flux is the Greek letter phi with subscript
Electric Flux Formula
The magnitude of this product is known as Electric flux, which is denoted by
So,
The electric flux through an area is the number of electric field lines passing normally through the area.

The formula of electric flux through an area, dA is given by
here,
Total flux through area A is
SI Unit of Electric Flux and Dimensional Formula
Flux is a scalar quantity so they can be added algebraically.
The SI unit of electric flux is newton meter squared per coulomb
Dimensional Formula
Electric flux=
thus dimension of electric flux are
|
Related Topics, |
Properties of Electric Flux
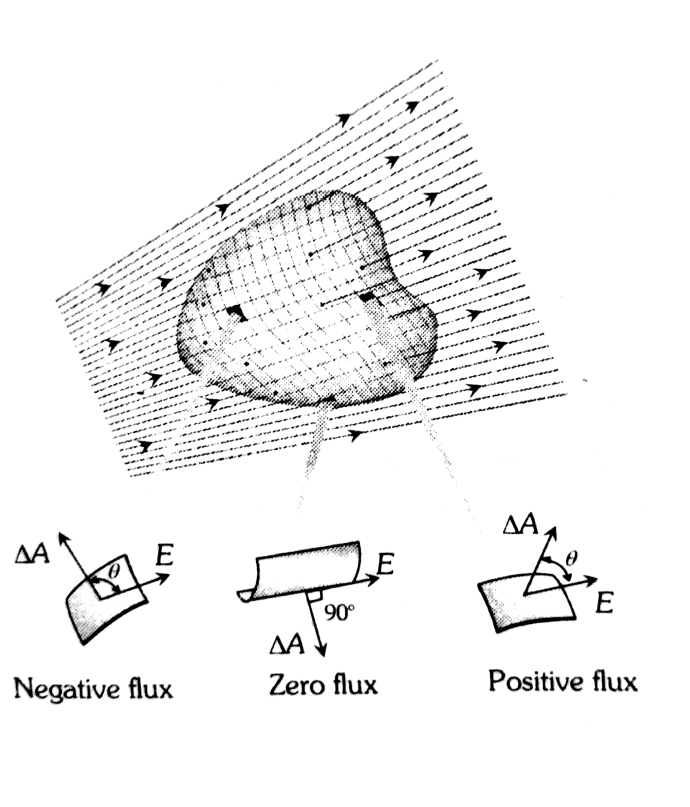
- The electric flux is dependent on the strength of the electric field and the field passing area.
- The flux is maximum at an angle
- The flux is minimum (zero) at an angle
- If the field lines are pointed outwards from the surface then the electric flux is positive. If they are pointed inward to the surface, the electric flux is negative.
- The total flux through a closed surface with no net charge is zero.
Electric Flux Density
Electric flux density is the amount of flux passing through a unit area in an electric field. Electric flux density is also called an electric displacement field. It is given as,
where,
- D is the electric flux density
- E is the electric field intensity
Gauss Law
Gauss's law states that in a closed surface, the electric flux is directly proportional to the total charge enclosed by the surface. Mathematically it can be expressed as,
where,
Derivation of Electric Flux Through a Closed Surface
To understand this concept, let us take an example
Consider a cylindrical surface of radius R, length

Here, the left end and electric field are making 180o, and the right end and the electric field are making
Similarly, we can find the electric flux through any closed surface by an electric field.
Also, read
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for All Subjects
- NCERT Notes For All Subjects
- NCERT Solutions for All Subjects
Solved Examples Based on Electric Flux
Example 1: A cone of base radius
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
Electric field
wherein
Area of
Example 2: The electric field in a region of space is given by,
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
Hence, the answer is the option (1).
Example 3: A cylinder of radius
1)
2)
3)
4) zero
Solution:
Electric field E through any area A
wherein

Flux through surface
Flux through cursurfacesaceC
Total flux through cylinder
Example 4: Electric field at a point varies as
1) An electric dipole
2) A point charge
3) A plane infinite sheet of charge
4) A line charge of infinite length
Solution:
Electric field E through any area A
wherein

Example 5: Total electric flux coming out of a unit positive charge put in air is:
1)
2)
3)
4)
Solution:
Flux may be Positive Negative or zero
For closed body.
wherein
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Flux is a chemical purifying agent, flowing agent or cleaning agent. Example: Ammonium chloride; Zinc chloride.
Electric flux, property of an electric field that may be thought of as the number of electric lines of force which intersect an area
Electric flux ϕE=EAcosθ. The SI unit of electric flux is Nm2/C
Magnetic Flux.
Electric flux.
Luminous Flux.
Radiant Flux.
Heat Flux.
Mass Flux.
Momentum Flux.
Acoustic Flux.
The direction of an electrical field at a point is the same as the direction of the electrical force acting on a positive test charge at that point.
Also Read
20 Nov'24 10:41 PM
15 Nov'24 04:55 PM
14 Nov'24 02:28 PM
14 Nov'24 12:28 PM
13 Nov'24 05:30 PM
11 Nov'24 07:17 PM
24 Sep'24 10:20 PM
24 Sep'24 10:12 PM
24 Sep'24 12:07 PM
19 Sep'24 01:55 PM


